Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Facilitation Techniques
- Coaching Techniques
- Mentoring
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to Scrum Master Core Competencies. As a Scrum Master, you play a pivotal role in guiding your team through Agile processes. This module will focus on three key competencies: Facilitation, Coaching, and Mentoring. You’ll learn how to effectively lead, support, and mentor your team to success while fostering an environment of collaboration, continuous improvement, and accountability.
Facilitation Techniques
Facilitation is a core responsibility of a Scrum Master. Your ability to guide discussions, ensure everyone’s voice is heard, and drive the team toward productive outcomes is essential for success.
Understanding Facilitation
- Definition: Facilitation is the process of enabling and guiding a group to achieve its goals without directing or controlling the outcome.
- Importance in Scrum: Facilitation ensures that the team can collaborate effectively, make decisions together, and move forward in alignment with Scrum principles.
- Facilitation vs. Directing: As a facilitator, your role is to support the team in reaching decisions themselves, rather than dictating what should be done.
Key Facilitation Techniques:
- Active Listening: Ensure that everyone’s perspective is heard and considered. Encourage participation and inclusivity.
- Open-Ended Questions: Stimulate deeper thinking and discussions by asking questions that require more than a yes/no answer.
- Time Management: Keep discussions focused and on track, ensuring that Scrum events don’t exceed their time-boxed limits.
Conflict Resolution and Visual Aids:
- Conflict Resolution: When conflicts arise, address them constructively by facilitating open communication and helping the team find mutually agreeable solutions.
- Visual Aids: Use diagrams, charts, and other visuals to enhance team understanding and streamline discussions.
Creating a Safe Environment:
- Trust and Open Communication: Build a safe environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and feedback.
- Ground Rules for Respect: Establish clear ground rules for respectful communication and interactions within the team.
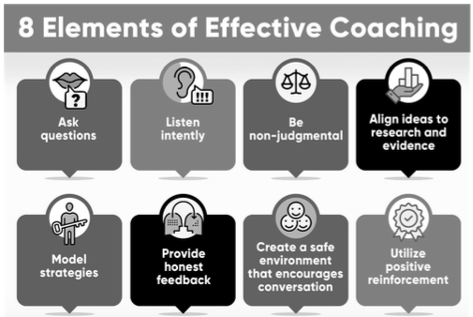
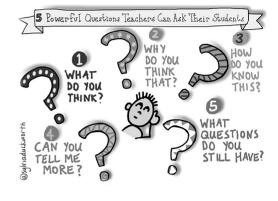
Coaching Techniques
As a Scrum Master, coaching is about helping team members realize their potential and guiding them to solve challenges independently. Coaching involves supporting individuals in achieving their goals while fostering a collaborative team environment.
Understanding Coaching:
- Definition: Coaching focuses on empowering individuals or teams to develop their own solutions and reach their full potential.
- Coaching vs. Mentoring vs. Managing: Coaching is short-term and goal-focused, while mentoring tends to be a long-term relationship. Coaching also differs from managing, as it’s less about directing and more about empowering.
- Supporting Team Potential: A Scrum Master helps the team unlock their potential through coaching conversations, feedback, and guidance.
Key Coaching Techniques:
- Active Listening: Understand the perspectives and challenges of team members by listening carefully and empathetically.
- Powerful Questions: Use insightful questions to help individuals reflect and solve problems independently.
- Goal Setting: Support individuals in setting and achieving SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound).
Feedback and Empathy in Coaching:
- Constructive Feedback: Offer feedback that encourages improvement and self-reflection.
- Empathy: Show genuine understanding and support for the challenges team members face.
Mentoring

Mentoring is a long-term relationship focused on personal and professional growth. While coaching focuses on immediate goals and challenges, mentoring looks at broader career and skill development.
Difference Between Mentoring and Coaching:
- Mentoring: A long-term relationship where the mentor offers advice and guidance based on their experience to support the mentee’s personal and professional development.
- Coaching: A more short-term relationship focused on achieving specific goals or overcoming immediate challenges, often through questioning and reflection.
Roles and Responsibilities in Mentoring:
- Mentor’s Role: Provide advice, share experiences, and support the mentee’s growth over time.
- Mentee’s Role: Be open to feedback, ask questions, and take responsibility for their learning and growth.
When to Use Mentoring vs. Coaching:
- Mentoring is best used when a long-term relationship is needed to guide career development or complex skill-building.
- Coaching is more suitable for immediate, short-term challenges that require focused solutions.
Conclusion
By the end of this module, you will have gained a solid understanding of the core competencies required to be an effective Scrum Master. These include:
- Facilitation: Guiding the team through Scrum events, fostering collaboration, and resolving conflicts.
- Coaching: Supporting team members in achieving their goals and developing problem-solving skills.
- Mentoring: Building long-term relationships to guide personal and professional growth.
Key Takeaways:
- Facilitation, coaching, and mentoring are essential competencies for any Scrum Master.
- Active listening, powerful questions, and empathy are critical skills in both coaching and mentoring.
- Creating a safe and collaborative environment helps the team thrive and continuously improve.
For more information on mastering Scrum Master competencies, visit the Scrum Guide and Artisan Agility.
